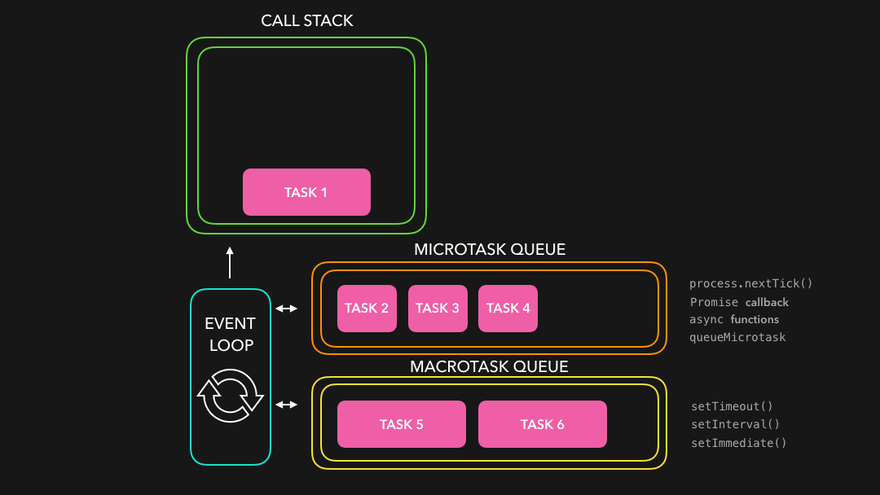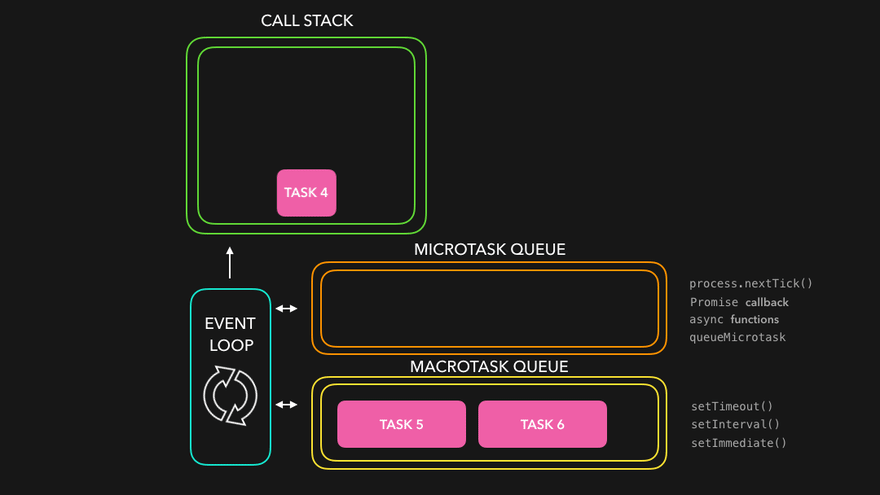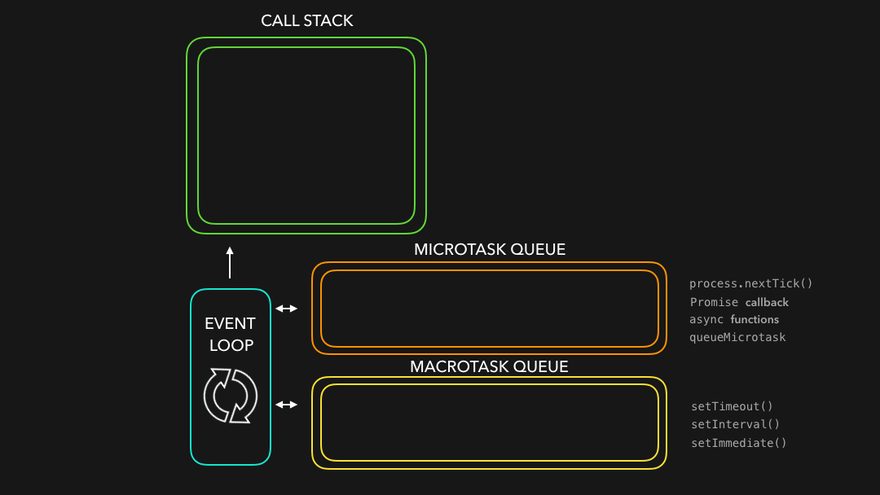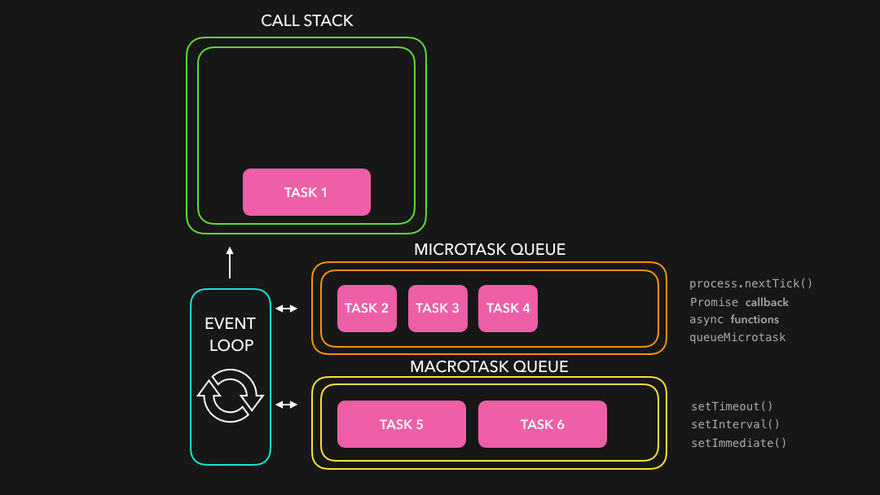
The package.json file is a crucial component of any Node.js project. It serves as the project's manifest file, providing metadata, configuration, and dependency information. In this article, we'll explore the various keys supported in package.json and their purposes in detail.
Why is package.json Important?
- Project Metadata: Provides details like the name, version, and author of the project.
- Dependency Management: Lists the libraries and tools required for the project.
- Script Automation: Defines custom commands for automating tasks like testing and building.
- Compatibility: Specifies compatible Node.js versions or other environment constraints.